The Kentucky Public Safety Peer Support Task Force was established by Senate Bill 64 to create a Best Practices Report and resources for the development of peer support programs. Each section of the report, as well as sample policies and other resources, are highlighted below. The entire best practices report can be downloaded
here
Peer support for public safety employees is the provision of emotional support by individuals who share similar experiences with the individual who has experienced trauma and/or a crisis. The services offered encompass a wide range of care.
 Need for Peer Support
Need for Peer Support
According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), public safety employees are at higher risk for psychological harm from the inherent traumatic incidents faced at work compared to the general population. Public safety employees frequently respond to such critical incidents as abuse, neglect, death, suicide, and other traumatic events.
 Benefits of Peer Support
Benefits of Peer Support
Evidence-informed research shows that peer support programs have positive benefits for public safety employees and can humanize mental health challenges, promote socialization, and reduce feelings of isolation and alienation. Having a trusted peer to confide in fosters hope and recovery and helps responders learn improved stress management techniques and coping skills which in turn creates greater resilience and employee engagement and addresses issues of cumulative stress.
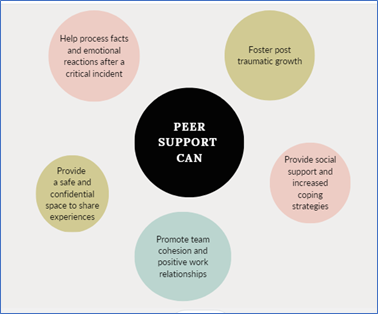
“The Value of Peer Support for First Responders” outlines the positive benefits of peer support programs. Studies that have investigated the benefits of peer support have found that peer support can help with the following :
 Establishing a Peer Support Program
Establishing a Peer Support Program
There are five core components to consider when establishing a peer support program: research and development, program design, implementation, maintenance, and evaluation.
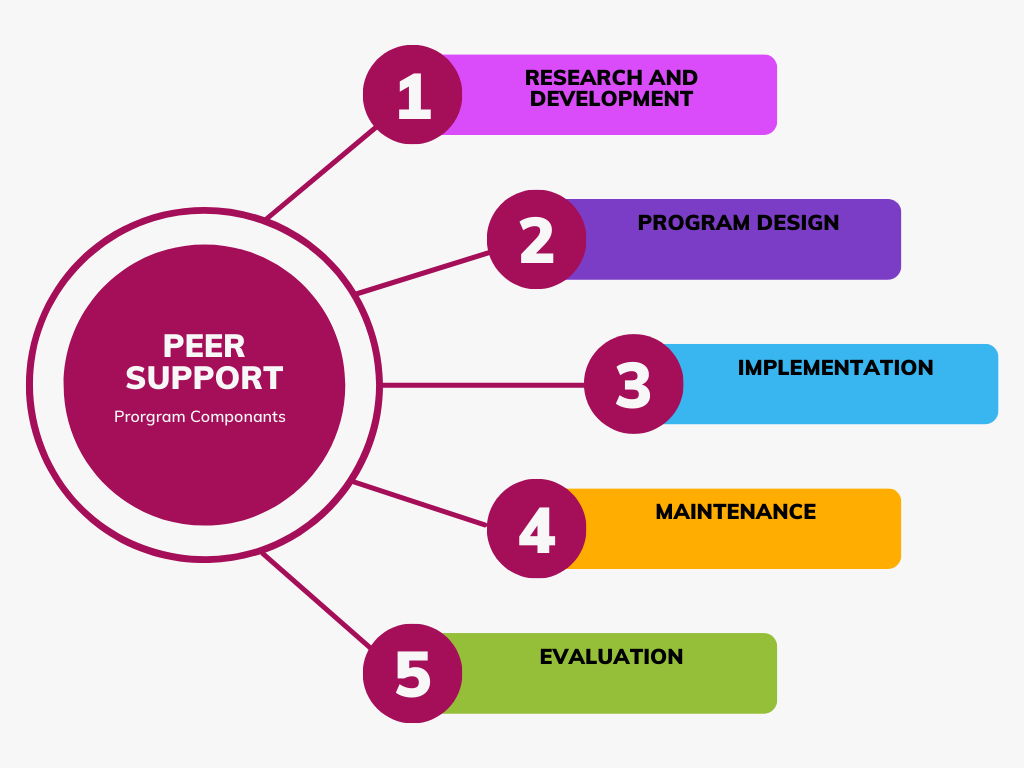
1 - Research and Development to Determine Organizational Readiness
- Conduct a needs assessment
- Determine stakeholder buy-in
- Locate and secure resources
2- Design the Program
- Develop protocols and procedures
- Establish roles, criteria, recruitment processes, and required training for peer supporters
- Create/select models for peer support interventions
3 - Program Implementation
- Reaching and engaging program participants
- Monitoring and supporting peer supporters
- Marketing the program
4 - Maintenance
- Create a plan for sustainability
5 - Evaluation
- Documenting processes
- Develop tools to evaluate outcomes/impact
 Operation of a public safety peer support program
Operation of a public safety peer support program
Ethical Standards
Because of the highly sensitive nature of the work of peer support programs, it is important to have clear ethical standards for the operation of the program and implementation by the peer support specialists. The first and foremost rule of peer support should be to “Do No Harm." Listed below are other defining factors that should go into any peer support program development:
- Provide a safe, comfortable, and neutral meeting space without leadership present. This includes county or city officials.
- Consider religious sensitivities. If a person brings up faith, listen with compassion and patience, affirm their values, and focus on stabilizing and normalizing the situation. Peer support meetings are not the time to discuss theology or docrtinal differences.
- Have a clear understanding of when participation will be required or not required.
- Develop a clear Conflict of Interest Policy and Statement for peer support specialists.
- Make sure there are measures in place to periodically assess the psychological well-being of peer support specialists.
- Create a method for reporting violations and sanctions.
- Make a protocol that peer support team members cannot provide services for a critical incident with which they were involved.
Confidentiality
Policies regarding confidentiality should be developed for all peer support programs that are consistent with state and federal laws, as well as organizational policies. Peer support team members should not keep formal written records of contacts with peers.
Sample Confidentiality Statement
Everything that is said during an intervention to a team member is confidential.
Team members will hold comments in the utmost confidence with the following exceptions:
-
If someone makes a statement of threat to harm themselves.
-
To bring harm to another person; or
-
Engage in a violent act.
If this should occur, team members are required to report such statements or threats to the proper authorities.
Additionally, we cannot guarantee that participants in this session will maintain confidentiality.
Establishing a matrix for training, continuing education, and recertification requirements for peer support specialists is critical. The matrix should list all required training, the number of hours of training required, and timelines for completion. In addition to training in active listening, stress management, and CISM techniques, peer support program team members should be trained in all policies and procedures of the program, including confidentiality, ethical standards, and referral for continued mental health services.
 Existing Programs
Existing Programs
Some larger police and fire agencies in the state have existing peer support programs. For smaller organizations thinking of starting a peer support program, there are groups that can help build capacity by assisting in a response.
 Sample Policies
Sample Policies
 Sample Confidentiality Policy.pdf
Sample Confidentiality Policy.pdf
 KACO Critical Incident Review and OIS.pdf
KACO Critical Incident Review and OIS.pdf
The following documents are standard operating procedures for Peer Support programs and include:
Definition of Peer Support including mission statement and vision.
Overtime policies for peer support specialists
Referral policy for further mental health services
Conflict of interest statement for peer support specialist
Criteria and process for selection of peer support specialist – include interview process, criteria for selection and deselection
Roles and Responsibilities of peer support specialists
Formal procedures for activation of and de-activation of the team
 Intl Assoc of Chiefs of Police Peer Support Operation Guidelines.pdf
Intl Assoc of Chiefs of Police Peer Support Operation Guidelines.pdf
 Sample Peer Support Policies.pdf
Sample Peer Support Policies.pdf
 1-10-peer-support-program.pdf
1-10-peer-support-program.pdf
 1037 Peer Support Program.pdf
1037 Peer Support Program.pdf
 Resources
Resources

Kentucky Public Safety Peer Support Task Force Members